
CT Scan
CT Scan (Computed Tomography) is a medical imaging technique that uses X-rays and computer technology to create detailed cross-sectional images of the inside of the body. These cross-sectional images allow physicians to obtain a 3D view of organs, bones, blood vessels, and soft tissues. CT scans are highly effective for diagnosing a wide range of conditions such as cancer, heart diseases, bone fractures, and trauma.
How CT Scan Works:
- The patient lies on the CT scanner’s table.
- The CT scanner emits X-rays from different angles toward the body.
- These X-rays pass through the body and are collected by sensors, then sent to a computer for processing.
- The computer processes the data and generates cross-sectional images of the body that can be viewed as thin slices or in 3D.
New CT Scan Modalities:
With advances in technology, CT scans have undergone significant updates, improving their accuracy, speed, and safety. Below are some of the new modalities and technologies in CT imaging:
-
Low-Dose CT Scan:
- This technology reduces the amount of radiation exposure, particularly useful for frequent screenings or use in children and radiation-sensitive individuals.
- Main application: Lung cancer screening, evaluating lung conditions, and diagnosing kidney and gallbladder stones with less radiation risk.
-
Cardiac CT (Coronary CT Angiography):
- This type of CT scan captures images of the heart and coronary arteries. It uses contrast agents to clearly show blood flow through the coronary arteries.
- Main application: Diagnosing coronary artery blockages or narrowing, heart disease evaluation, and assessing heart attacks.
-
Dual-Energy CT:
- This technique uses two different energy levels of X-rays to provide better distinction between various tissues and contrast agents.
- Main application: More accurate diagnosis of kidney stones, evaluating soft and hard tissues, tumor detection, and tissue analysis.
-
Volume CT:
- This advanced technique collects a large amount of imaging data in 3D from different areas of the body in a short time. It provides high-resolution images with faster processing times.
- Main application: Rapid assessment in emergencies, trauma, organ evaluation with high detail, and precise tumor diagnosis.
-
Spectral CT:
- Using data from different X-ray energy levels, this modality differentiates tissues based on their chemical composition.
- Main application: More accurate tumor diagnosis, kidney and gallbladder stone assessment, and determining tissue composition.
-
4D CT (Dynamic CT):
- This modality allows continuous imaging of organs and tissues over time, enabling physicians to observe dynamic changes in function and movement.
- Main application: Lung function imaging, tracking tumor movement, and real-time heart function assessment.
-
-
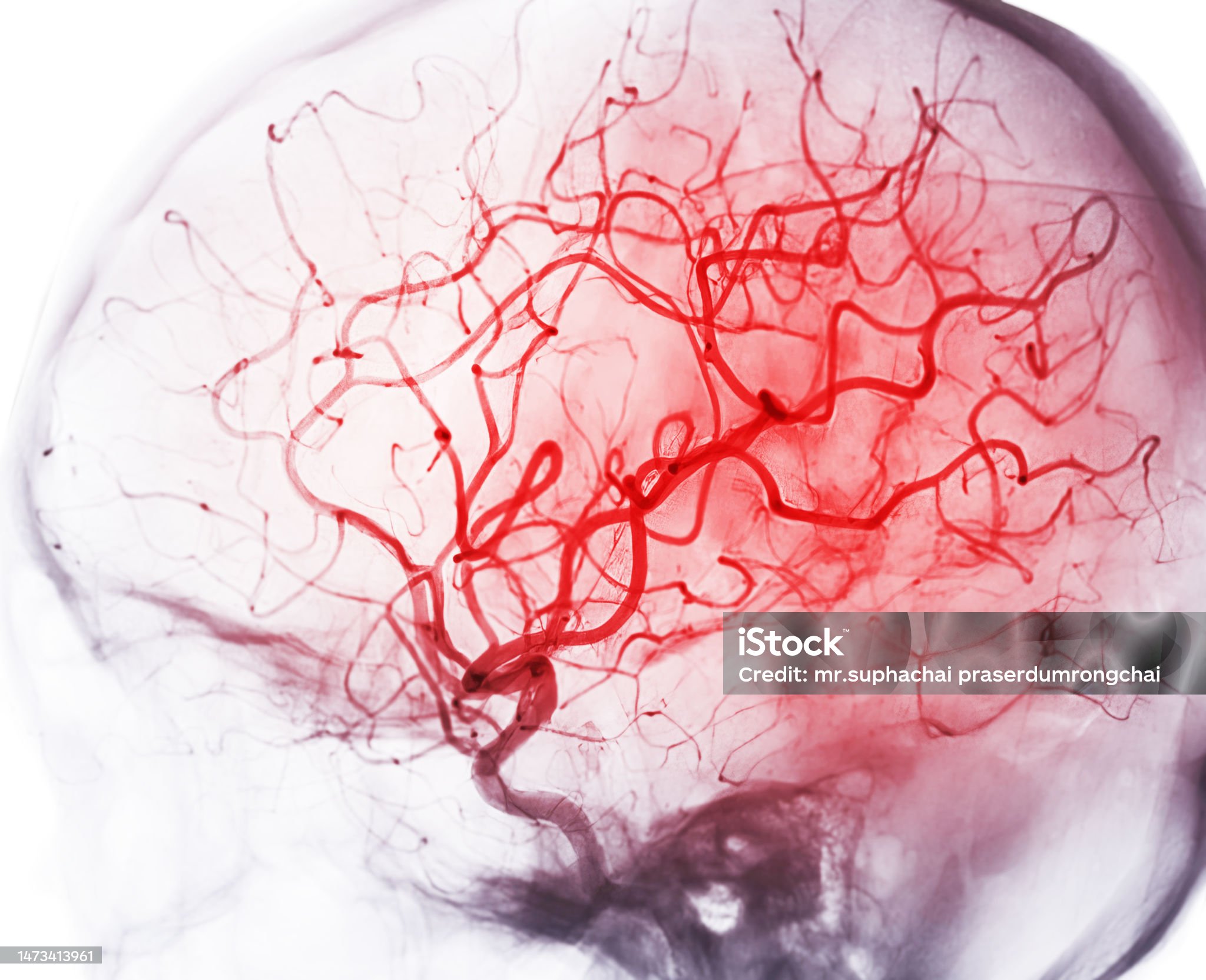
CT Angiography (CTA):
- This modality uses contrast agents to image blood vessels. CT angiography provides detailed visualization of vascular structures and function.
- Main application: Diagnosing vascular diseases such as aneurysms, blockages, and evaluating coronary and cerebral vessels.
-
Whole-Body CT Scan:
- This modality allows doctors to image the entire body in one session and within a short period. It is particularly useful for patients who need rapid and comprehensive assessment.
- Main application: Trauma assessment, cancer detection, and evaluating metastasis throughout the body.
Advantages and Modern Applications of CT Scanning:
CT scans, with their new advancements, have become an essential tool for diagnosing and treating diseases. Some key benefits include:
- Fast imaging: CT is especially useful in emergency situations where a quick diagnosis is necessary.
- High accuracy in displaying different tissues: This technology can clearly display both hard tissues like bones and soft tissues like organs.
- 3D assessment: The 3D images produced by CT scanning allow physicians to evaluate complex areas of the body with high precision.
- Wide range of applications: From diagnosing tumors and heart conditions to evaluating traumatic injuries and assessing kidney stones and vascular conditions.
With these advancements, CT scanning continues to be one of the most widely-used and advanced imaging techniques, and with new modalities, it offers more precise and safer diagnosis and treatment of complex diseases.



